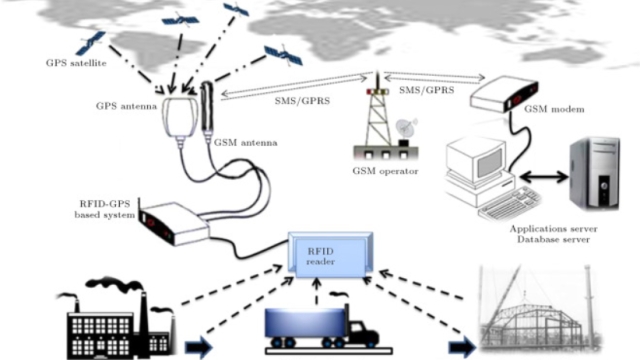
Welcome to a world where every object is connected, communication is seamless, and tracking becomes effortless. This is the future promised by RFID technology. RFID, or Radio Frequency Identification, has emerged as a revolutionary solution to bridge the gap between the digital and physical realms. With its ability to wirelessly identify and track objects with embedded RFID tags, this technology holds immense potential for transforming industries and our everyday lives.
At its core, RFID technology operates by utilizing radio waves to transmit information between RFID tags and readers. These tags, which are equipped with tiny microchips and antennas, can be attached or embedded in various objects such as products, assets, or even living beings. When an RFID reader emits radio waves, the nearby tags respond by transmitting their unique identification code and any additional data they store. This two-way communication enables real-time tracking, monitoring, and inventory management on a scale previously unimaginable.
Applications of RFID Technology
RFID technology has revolutionized various industries with its versatility and efficiency. From inventory management to contactless payment systems, RFID technology has found its way into numerous applications.
Retail and Inventory Management:
RFID technology is widely used in the retail industry for inventory management purposes. By attaching RFID tags to products, retailers can track and monitor their inventory with ease. This technology enables real-time visibility into stock levels, allowing businesses to maintain optimal inventory levels and streamline the replenishment process. Additionally, RFID tags can be used to prevent theft by triggering alarms when products leave the store without being purchased.Supply Chain and Logistics:
In the logistics and supply chain industry, RFID technology plays a crucial role in improving efficiency and accuracy. By using RFID tags, companies can track and trace products throughout the entire supply chain. This helps enhance inventory accuracy, reduce the risk of errors, and expedite the shipping and receiving process. Additionally, the real-time data provided by RFID technology allows for better demand forecasting and inventory planning, leading to cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.Access Control and Security:
RFID technology is widely utilized for access control and security purposes in various settings. From office buildings to hotels and amusement parks, RFID-based access control systems enable convenient and secure entry for authorized individuals. By using RFID cards or key fobs, users can easily gain access to restricted areas, replacing traditional lock and key systems. Furthermore, RFID-based security systems can be employed to track personnel movements and monitor access logs, adding an extra layer of security.
RFID technology’s potential extends beyond these applications, and its adoption is continuously expanding into new domains. As businesses and industries continue to explore and innovate with this technology, we can expect even more exciting applications to emerge in the near future.
Advantages and Limitations of RFID
Advantages
RFID technology offers several advantages that make it a powerful tool in various industries. Firstly, RFID tags are capable of storing and transmitting large amounts of data, allowing for efficient tracking and authentication of items. This capability significantly enhances supply chain management, inventory control, and asset tracking systems.
Secondly, RFID technology enables automation and scalability. With the ability to read multiple tags simultaneously, RFID systems can streamline processes and increase operational efficiency. This makes it particularly useful in environments where real-time tracking and monitoring are essential, such as logistics, retail, and healthcare.
Lastly, RFID technology has a non-line-of-sight capability, which means tags can be read and interrogated even when they are not directly visible. This makes RFID suitable for applications where traditional barcode scanners or manual data entry would be impractical or time-consuming, such as tracking assets in warehouses or monitoring the movement of goods within a manufacturing facility.
Limitations
Despite its advantages, RFID technology also has limitations that need to be considered. One limitation is the cost of implementation. RFID systems can require significant upfront investment, especially when integrating with existing infrastructure and deploying network infrastructure to support the technology. This cost can be a barrier for small businesses or organizations with limited financial resources.
Another limitation is the issue of data security and privacy. As RFID tags transmit data wirelessly, there is a potential risk of unauthorized access or interception of sensitive information. Protecting data integrity and ensuring privacy is crucial in RFID deployments, and appropriate security measures must be put in place to mitigate these risks.
Lastly, RFID technology faces some challenges in terms of tag readability. The presence of metal, liquids, or other materials can interfere with the performance of RFID tags, reducing their readability. This can be problematic in certain environments, such as those with high moisture content or where items are stored near metallic surfaces.
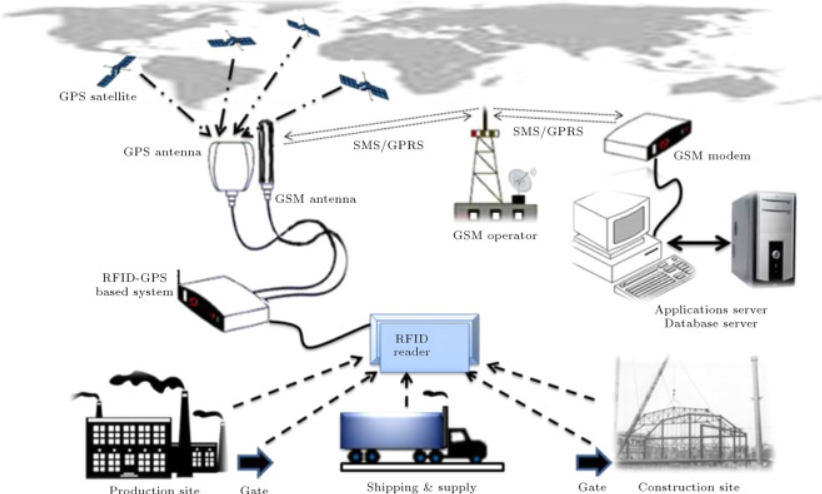
Overall, while RFID technology holds great promise in revolutionizing various industries, it is important to weigh its advantages against its limitations and consider the specific requirements of each implementation to ensure successful deployment.
Implications for the Future
RFID technology has the potential to revolutionize various aspects of our lives, bringing about significant changes in the future. From inventory management to supply chain optimization, its applications are vast and promising.
One key implication of RFID technology is its impact on retail operations. With RFID tags embedded in products, retailers can effortlessly track and manage inventory. This enables real-time visibility of stock levels and reduces the need for manual stocktaking. As a result, businesses can streamline their operations, maximize efficiency, and provide a seamless shopping experience for customers.
Another area where RFID technology shows great promise is in healthcare. By utilizing RFID tags on medical equipment and patient wristbands, hospitals can enhance patient safety and improve workflow management. Accurate identification and tracking of medical assets can help prevent errors, reduce costs, and ultimately save lives. Moreover, RFID-enabled patient monitoring systems can provide valuable insights for healthcare providers, facilitating personalized and proactive patient care.
RFID tags
Furthermore, RFID technology can play a crucial role in enhancing logistics and transportation systems. By using RFID tags on packages, shipping companies can streamline the tracking and delivery process. This enables faster and more efficient shipment handling, reducing delays and improving overall customer satisfaction. Additionally, the integration of RFID technology with smart cities initiatives can lead to smarter traffic management and improved public transportation services, benefiting urban living.
In conclusion, the future implications of RFID technology are vast and promising. From revolutionizing retail operations to improving healthcare and enhancing logistics, RFID has the potential to reshape various industries. As we embrace this technology and explore more innovative applications, we can look forward to a future where efficiency, accuracy, and convenience are seamlessly woven into our everyday lives.