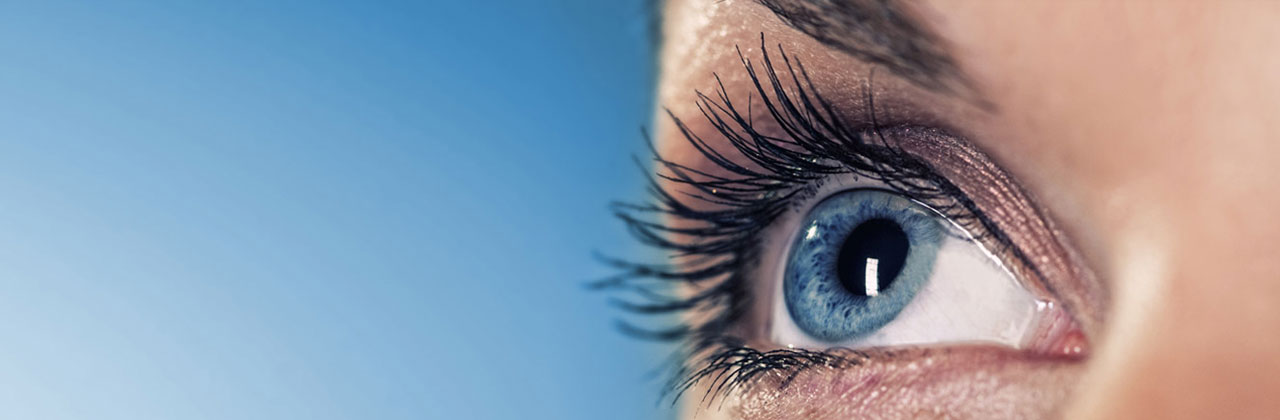
Retinopathy is a condition that affects the eyes, specifically the retina, and it is an important area of study in the field of ophthalmology. It is often associated with certain underlying health conditions such as diabetes. Diabetic eye screening is one of the methods used to detect retinopathy at an early stage, enabling timely and effective treatment. While retinopathy can lead to vision impairment or even blindness if left untreated, understanding its causes and symptoms can help individuals take proactive measures to prevent or manage this condition. Additionally, recognizing the potential link between retinopathy and other eye conditions, such as glaucoma, can further enhance our understanding and approach to these conditions. By shedding light on the shadows surrounding retinopathy, we can equip ourselves with the knowledge needed to promote healthier vision and overall well-being.
1. The Importance of Diabetic Eye Screening
Regular diabetic eye screening is crucial for individuals with diabetes in order to detect and manage complications such as retinopathy and glaucoma. Diabetic eye screening, conducted by ophthalmologists, involves a thorough examination of the eyes to identify any signs of damage or abnormalities caused by diabetes. This screening is essential because it allows for early detection and treatment, preventing further deterioration of the eyesight.
Retinopathy, a common complication of diabetes, occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina. If left untreated, retinopathy can lead to vision loss or blindness. Regular eye screenings enable ophthalmologists to identify retinopathy at early stages, allowing for timely intervention and the implementation of effective treatment strategies.
Furthermore, diabetic eye screening is not limited to the detection of retinopathy alone. It also helps identify the presence of glaucoma, another eye condition that can result in vision impairment. Glaucoma is characterized by increased pressure within the eye and can damage the optic nerve, leading to gradual vision loss. Through routine eye screenings, ophthalmologists are able to diagnose and manage glaucoma, helping patients maintain their visual health.
In summary, the importance of diabetic eye screening cannot be overstated. By regularly visiting ophthalmologists for comprehensive eye examinations, individuals with diabetes can ensure early detection and treatment of retinopathy and glaucoma. These screenings play a vital role in preserving vision and preventing irreversible eye damage.
2. Understanding Retinopathy: Causes and Symptoms
Retinopathy is a condition that affects the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. It often occurs as a complication of certain systemic diseases, with diabetes being the most common underlying cause. When the blood vessels within the retina are damaged, it can lead to vision problems and potentially vision loss if left untreated.
The primary cause of retinopathy lies in the sustained high levels of glucose in the blood, which is particularly relevant for individuals with diabetes. Over time, these elevated glucose levels can harm the blood vessels that supply the retina, leading to a condition called diabetic retinopathy. Additionally, other factors such as high blood pressure, smoking, and high cholesterol levels can contribute to the development and progression of retinopathy.
Symptoms of retinopathy may vary depending on the stage and severity of the condition. In the early stages, individuals may not experience any noticeable symptoms. As retinopathy progresses, common symptoms can include blurred or distorted vision, the appearance of floaters or dark spots in the visual field, difficulty seeing colors, and even complete vision loss in severe cases.
Regular eye screening, especially for individuals with diabetes, is crucial to detect retinopathy at an early stage. Ophthalmologists can conduct various tests to assess the health of the retina and identify any signs of retinopathy or other eye conditions such as glaucoma. Early detection allows for prompt intervention and management of retinopathy, potentially preventing further vision deterioration and complications.
See More
3. Managing and Treating Retinopathy
In order to effectively manage and treat retinopathy, it is crucial to prioritize regular ophthalmology screenings for individuals at risk, particularly those with diabetes. These screenings play a pivotal role in early detection and intervention. By identifying retinopathy at an early stage, treatment interventions can be implemented promptly, significantly reducing the risk of further vision impairment or even blindness.
One of the key approaches to managing retinopathy is through careful control and management of diabetes. Maintaining stable blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol is paramount to minimize the progression of retinopathy. Patients are usually advised to follow a balanced diet, engage in regular exercise, and take prescribed medication to regulate their blood glucose levels effectively.
Another crucial aspect of managing retinopathy lies in the use of laser therapy. Laser treatment, such as photocoagulation, can be employed to seal off leaking blood vessels or destroy abnormal ones. This procedure helps to prevent further damage to the retina and preserve vision. Additionally, anti-VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) injections have shown promising results in managing retinopathy by inhibiting the growth of abnormal blood vessels, reducing swelling, and improving overall vision.
Furthermore, it is important to address any underlying conditions that contribute to retinopathy, such as glaucoma. When managing retinopathy, treating coexisting eye conditions ensures comprehensive care and better outcomes. By identifying and treating glaucoma alongside retinopathy, vision loss can be further minimized.
By adopting a multidisciplinary approach that involves regular screenings, diligent diabetes management, laser therapy, and addressing associated eye conditions, individuals with retinopathy can effectively manage the condition and protect their vision for a better quality of life.