Captive insurance: Unlocking Strategic Financial Freedom
As businesses strive to manage risks and protect their assets, the concept of captive insurance has gained considerable attention. Captive insurance is a powerful risk management tool that allows companies to take more control over their insurance needs. By creating their own insurance companies, known as captives, businesses can tailor coverage to their specific requirements, ultimately enhancing their financial stability and autonomy.
One notable provision that has contributed to the rise of captive insurance is the IRS 831(b) tax code. This particular section of the tax code provides specific benefits to microcaptives, which are captives with annual premiums not exceeding $2.3 million. Under this provision, microcaptives can elect to be taxed only on their investment income, offering potential tax advantages that incentivize businesses to explore captive insurance as a viable strategy.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of captive insurance, exploring how it operates, its benefits, and the regulations imposed by the IRS. We will also delve deeper into the IRS 831(b) tax code to provide a comprehensive understanding of its implications for businesses considering or already utilizing captive insurance. By unlocking the potential of captive insurance and harnessing strategic financial freedom, businesses can safeguard their assets, manage risks effectively, and bolster their long-term success. So, let’s embark on this journey into the world of captive insurance and discover how it can transform your business.
Understanding Captive Insurance
Captive insurance is a unique and strategic financial tool that has gained significant attention in recent years. It revolves around the concept of forming an insurance company to cover the risks of its parent organization or a group of related entities. One of the key benefits of captive insurance is the ability to design customized insurance programs tailored to specific needs.
At the heart of captive insurance is the utilization of Section 831(b) of the IRS tax code, which provides certain tax advantages for small insurance companies. Known as microcaptives, these entities can elect to be taxed only on their investment income, rather than their underwriting income, subject to meeting specific IRS criteria. The 831(b) tax election offers potential tax savings for businesses looking to manage their insurance risks efficiently.
Captive insurance allows corporations to gain more control over their risk management strategies. By establishing their insurance company, organizations can customize coverage, set underwriting guidelines, and directly participate in the profits generated by their insurance program. This level of control fosters a sense of self-reliance and provides financial freedom in managing insurance-related costs effectively.
In summary, captive insurance offers businesses the ability to form their insurance company, providing flexibility, tax advantages, and risk management customization. By leveraging the benefits of captive insurance, organizations can enhance their financial strategies and embark on a path towards greater financial independence.
Benefits of 831(b) Captive Insurance
Section 2 of 3 sections
Captive insurance under the 831(b) tax code offers several enticing benefits that can substantially impact a company’s financial landscape. Let’s explore three key advantages of implementing a captive insurance strategy.
Enhanced Risk Management:
By forming a captive insurance company, a business gains more control over its insurance coverage, policies, and premium costs. Unlike traditional insurance providers, captives allow for flexible and tailored coverages that align precisely with the company’s specific risk profile. This strategic advantage enables businesses to effectively mitigate risks, protect their assets, and safeguard against potential economic losses in a more efficient manner.
Tax Advantages:
One of the most significant benefits of utilizing a captive insurance solution is its favorable tax treatment under the 831(b) tax code. Captive insurance premiums paid by a company to its own captive are typically deductible for tax purposes, reducing taxable income and ultimately decreasing the overall tax liability. This creates an opportunity for businesses to optimize their tax planning strategies, lowering their tax burden while simultaneously strengthening their financial position.
Improved Cash Flow:
Implementing a captive insurance program offers the potential for improved cash flow management. Rather than paying premiums to third-party insurers, businesses retain these funds within their captives, allowing them to build reserves and accumulate wealth over time. With greater control over claims and the ability to retain underwriting profits, companies can potentially experience more stable insurance costs, resulting in enhanced financial flexibility and increased cash flow to support growth and investment initiatives.
In conclusion, the utilization of a captive insurance strategy under the 831(b) tax code presents businesses with multiple benefits, including enhanced risk management capabilities, advantageous tax treatment, and improved cash flow management opportunities. By strategically leveraging these benefits, businesses can unlock new avenues of financial freedom and drive sustainable growth.
Compliance and Regulations for Microcaptives
When it comes to microcaptives and captive insurance, compliance and regulations play a crucial role. It is important for businesses considering setting up a microcaptive to understand and adhere to the rules established by the IRS 831(b) tax code.
Explore
The IRS 831(b) tax code provides certain tax advantages to microcaptives, making them an attractive option for businesses looking to manage their risks effectively. However, it is essential to comply with the specific requirements outlined in the tax code to maintain these benefits. Failure to do so can result in penalties and the loss of tax advantages.
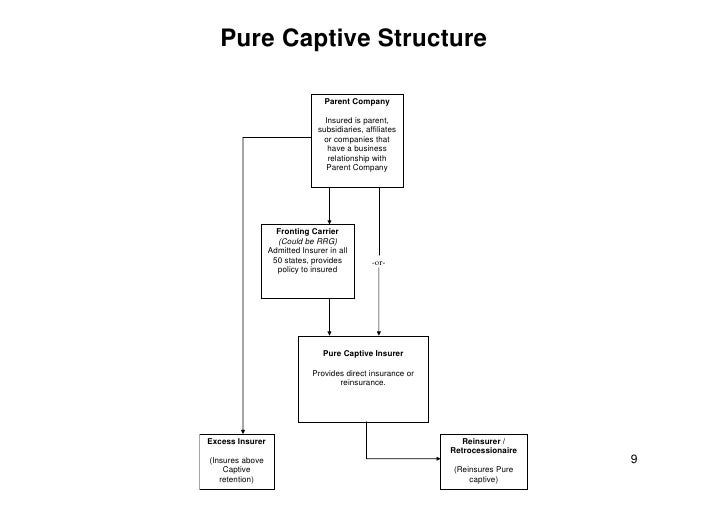
One key aspect of compliance is ensuring that the microcaptive is adequately structured and operates as a legitimate insurance company. This includes maintaining separate books, underwriting policies that reflect the transfer of risk, and demonstrating sufficient capitalization.
Additionally, it is crucial to navigate various regulatory requirements that may apply to microcaptives. While captive insurance entities are generally regulated at the state level, specific regulations can vary depending on the jurisdiction in which they are established. Understanding and adhering to these regulations is essential to ensure compliance with local laws and regulations.
By complying with the IRS 831(b) tax code and relevant regulatory requirements, businesses can leverage the benefits of captive insurance while remaining within the bounds of the law. It is recommended to consult with knowledgeable professionals, such as tax advisors and insurance specialists, to ensure adherence to compliance and regulatory obligations throughout the establishment and operation of a microcaptive.